For a rider, shifting on a motorcycle is one of the most vital techniques to learn. Most motorcycles, in fact, have a manual gearbox that must be shifted by manual intervention and requires coordination of the clutch, throttle, and gear lever. It may seem almost impossible at first.However, once the rider attains the rhythm, logic, and coordinative feel for the shift, it just becomes a way of life. This guide will provide quite useful tips for a first timer or the experienced rider who wishes to fine-tune their existing gear shifting skills.
Tabla de contenido
PalancaMotorcycle Gear Shifting Understanding
Before delving into detail, let’s see the basics of shifting gears motorcycle:
Shifting on a Motorcycle
Motorcycle shifting means changing gears to align the power of the motorcycle’s engine with your speed. The vast majority of motorcycles use a sequential gearbox, meaning gear changes happen in sequence; you cannot, like in a car, skip a gear.
The shifts are typically performed by the following system:
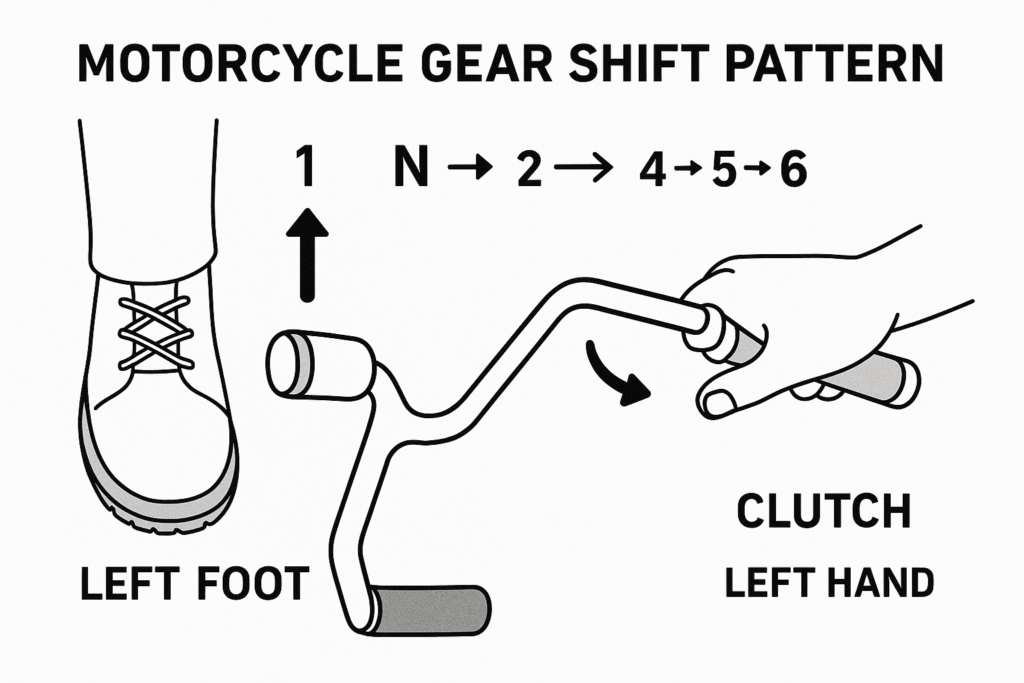
- 1st gear (down) – Neutral (half-click up) – 2nd to 6th gear (full clicks up)
- It is often written as 1 – N – 2 – 3 – 4 – 5 – 6.
A shift will be done using your left foot on the gear lever while your left hand engages the clutch.
Essentially, the change gear motorcycle process involves the left hand pulling in the clutch lever, the left foot clicking the gear shifter, and lastly the right-hand control of the throttle. The motorcycle’s shifting is much more intuitive after you have practiced than a car with SD and clutches because your hands and feet are always in position.
How Proper Gear Shifting Could Be Critical
Proper shifting will ensure that you make the best use of your motorcycle’s engine. Poorly timed and rough shifts are the bane of every motorcycle’s internal structures; they shorten lifespan, raise fuel consumption, and create a sense of instability. For example, early shifting may cause lugging or vibration and poor pickup, while late shifting wastes fuel and probably runs the risk of over-revving the engine.
How Do You Shift on a Motorcycle?
Let’s look at a detailed guide on how to shift on a motorcycle:
Step 1 – Starting the Bike and Getting into First Gear
To begin with, pull the clutch lever fully with the left hand while the bike is in neutral. Take your left foot and press the gear-shifter down into first gear. Gradually release the clutch and gently roll on the throttle. This combination allows the engine power to transfer smoothly to the wheels. Remember to be patient, many beginners stall here.However, with practice, you will learn to balance between the two.
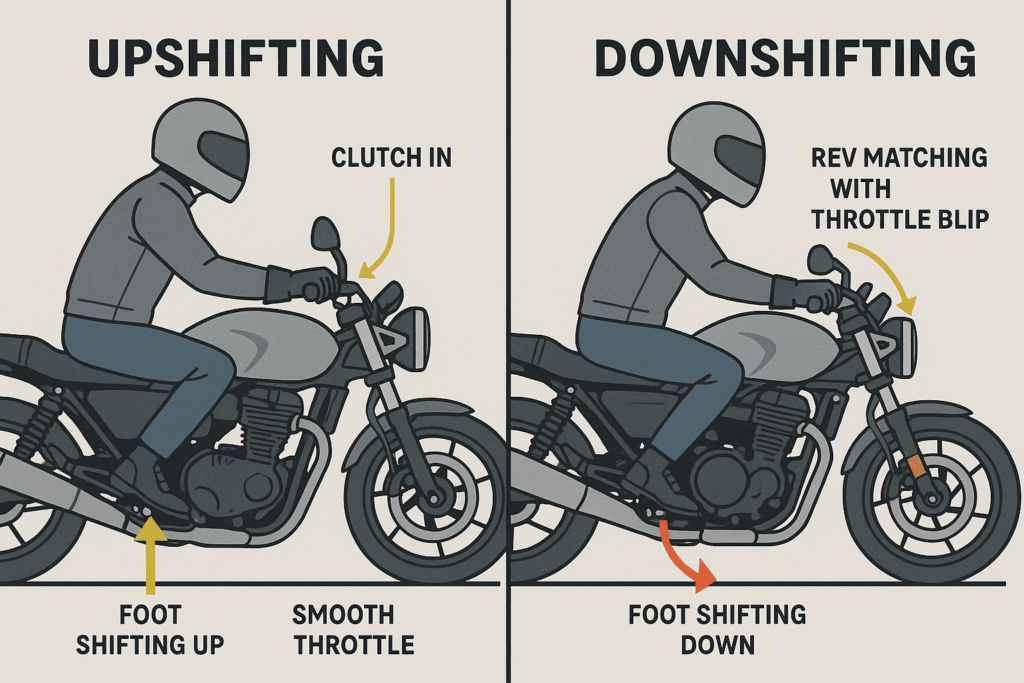
Step 2- Upshifting While Riding
The moment you feel that the bike is moving and the engine RPMs are climbing, it is time to shift up. Shifting between 5000-7000 RPM is ideal, depending on your bike. Depress the clutch, gently toe the shifter up to the next gear, then smoothly release the clutch while rolling back onto the throttle. This would maintain a constant delivery of power and an overall smooth transition, free from jerking/movement.
A common question among the riders would be, “When should I shift?” Here is a rough approximation:
- 1st gear: 0–15 km/h
- 2nd gear: 15–30 km/h
- 3rd gear: 30–45 km/h
- 4th gear: 45–60 km/h
- 5th/6th gear: Above 60 km/h (for cruising on highways)
It may differ based on the power and load of your bike.
Step 3: Downshifting Technique
Downshifting refers to slowing down or stopping. Start by rolling off the throttle and pulling in the clutch. Click the gear lever down and gently release the clutch while matching the engine speed. Rev matching will come into play at this point, giving the throttle a slight blip before releasing the clutch, which prevents sudden engine braking and allows your ride to remain smooth.
Advanced Motorcycle Shifting Techniques
Now, let’s see some advanced motorcycle shifting techniques:
What Is a Quick Shifter Motorcycle and How Does It Work?
A quick shifter allows you to change gear on motorbike without using the clutch or closing the throttle by an electronic device. The quick shifter temporarily cuts the ignition or fuel supply so the gearbox is loosened just enough to allow shifting gears almost instantaneously. These are an advanced feature that began to be employed on race bikes, so the new rider should work on manual shifting.
Clutchless Shifting on Motorcycles – Is It Safe?
As the name suggests, shifting gears without using the clutch is called clutchless shifting. In fact, this is one of the preferred ways of upshifting for advanced motorcyclists. If done correctly with respect to timing and throttle, this shifting should be smooth and sweet. Downshifting without the clutch can be risky and should probably be best done only by the pros. Improper use of clutchless shifting will take a toll on the transmission, so it’s best suited for the confident rider or when riding those performance-oriented bikes designed to handle this.
Automatic Transmission Motorcycle Gear Shifting
An automatic motorcycle does not require a clutch or manual gear control like conventional bikes. Change of gears is rather done automatically by means of a CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission).
Riding is simple, just:
1. Twist the throttle to go.
2. Let go of the throttle to slow down.
3. The brakes work the same way as on a normal bike (right hand = front brake, right foot = rear brake).
In gear positions, you can relax, a bike takes care of all gear changes. This becomes more like an art, which is more helpful for new riders, especially in traffic and on inclines.
Gear Shifting Skills in an Emergency
In emergencies, quick thinking and gear-making may keep you alive. Some advice:
Sudden stop: Pull the clutch and quickly downshift while applying brakes to prevent stalling.
For slippery roads: Work on the higher gears to cut wheelspin; do not do sudden gear changes.
Engine braking: Downshift gently to help in slowing the bike when brakes are insufficient.
Bike not moving: If you are stuck in a high gear, downshift to first gear.
You will train yourself to respond quickly with practice, so find safe areas to prepare for the times that count.
Common Gear Shifting Mistakes and Their Prevention
Following are some of the gear shifting mistakes along with some tips to avoid them:
Top Beginner Mistakes
One of the most common mistakes is shifting far too early or too late. Shifting at low RPM means that the engine will struggle, whereas shifting at high RPM will often result in jerks and noise. Clutch releases too quickly, creates sudden delivery of power, and can also wash out the engine. Another common mistake is looking down at your gear lever while riding, usually because it breaks concentration and delays reaction times.
Troubleshooting Bad Shifting Behavior
Is your bike grinding when shifting gears or jerking around? You might be missing some shifts or a misadjusted clutch. These problems can occur due to the following reasons: worn clutch cables, poorly positioned feet, or throttle mis-time changes. These are usually fixed with little maintenance and by simply riding more mindfully.
Motorcycle Gear Shifting for Different Bikes and Terrains
Let’s see how different bikes have different gear shifting techniques:
Street Bikes vs Dirt Bikes vs Cruisers
Street bikes usually have a closer gear ratio that requires more frequent shifts while in traffic. Dirt bikes are designed with wider gear ratios. They are well poised for tremendous acceleration from a state of rest on loose surfaces. Cruisers, however, provide heavy-torqued engines perfect for relaxed shifting at lower RPMs.
The style of changing gears on a motorcycle, according to the types of bikes, dirt bike riders would shift aggressively and quickly; this is especially true in races. Cruisers enjoy a very laid-back, relaxed approach to shifting.
Shifting During Hills, Wet Roads, and Corners
Downshifting very early affords more torque when riding uphill. On wet roads, abrupt movements, either with a throttle change or shift, may induce tire slips. Always change before entering a turn, because in mid-turn, there may very well be a disturbance of balance and traction.
Shifting Characteristics in Subcategories of Motorcycles
Small motorcycles ranging from 125 cc o 150cc have smooth and forgiving gearboxes for city rides and new riders, not requiring drastically high RPMs or aggressive shifts, whereby learning becomes easier. The 300-500cc range is already responding better to higher RPMs and speed, making it a lot more reasonable for daily commuting and highway rides.
When you get up to the 600cc class, especially with sport or adventure bikes, the gear ratios are tighter and the throttles more sensitive. These machines reward timing and precision in the transition between gears, especially on acceleration. The performance potential of the machines is phenomenal, yet it takes a rider with a deliberate skill set to go there with confidence.

Motorcycle Gear Explained: What Gear to Use and When
Of course, not all gears fit at all speeds. Lower gears in city traffic (1 to 3) allow better control because, with large speeds, fifths and sixths only give very good efficiency with lower engine wear. The rule of thumb is to shift based on speed and engine sound. Listen to how your bike sounds. If it strains, downshift, suppose it revs too highly but isn’t going much faster, upshift. Learning that feeling takes practice, but it definitely will make shifting second nature.
Gear vs. RPM vs. Speed (city and highway)
Gear | RPM Range | Speed (City) | Speed (Highway) |
1st | 2,000–5,000 | 0–15 km/h | – |
2nd | 3,000–6,000 | 15–30 km/h | – |
3rd | 4,000–6,500 | 30–45 km/h | 40–50 km/h |
4th | 4,500–7,000 | 45–60 km/h | 50–65 km/h |
5th | 5,000–7,500 | – | 60–80 km/h |
6th | 5,000–8,000 | – | 80+ km/h |
How Many Gears Do Motorcycles Have?
Generally, a motorcycle can have five to six gears, based on the model. Entry-level motorcycles usually have fewer gears, while high-performance machines utilize six-speed transmissions for finer control. Modern gearboxes are, of course, rugged and very accurate, but they require constant care.
Tools & Accessories to Elevate Shifting Quality
The following are some of the important tools and accessories to elevate shifting qualities:
Aftermarket Quick Shifters and Gear Indicators
Installable onto compatible bikes, quick shifters improve shifting speed. Gear position indicators are also great, especially for new riders. Both upgrades are ways of avoiding mistakes and giving a confidence boost.
Maintenance Tips for Better Shifting
Always check if your clutch cable is properly adjusted; it should not be loose or too tight. Regular changes apply to the cable, or it should be lubricated, as necessary. Regular checks of the transmission oil should be done, with emphasis on using the right grade. Lack of lubrication tends to cause missed shifts and damage over time.
Precision Gear Systems Inspired by Competition
These BSEMotor motorcycles are built following the tenets of competitive off-roading. Each BSEMotor motorcycle specifically embodies responsive gear shifting systems and is fit with superbly rugged transmissions all made for high-performance riding. This precision gear technology affords you confidence while negotiating any trail-tight or urban roads.
Opportunities for Partnership with BSEMotor
At BSEMotor, we offer more than just machines. We have motorcycles and scooters equipped with custom-designed gear systems and packaged for private labeling and custom tuning.
Partners get:
- Expert mechanical tuning
- Bulk purchase options
- Dedicated support to technical issues
- Global shipping and International servicing.
With BSEMotor, you are putting your business in line with a brand synonymous with accuracy, performance, and reliability.
Preguntas frecuentes
How to Shift Smoothly on a Motorbike?
To shift without rattling gears, cut the throttle, gently pull the clutch in, shift, release the clutch while putting back the throttle. In time, that rhythm will become second nature.
What Really Happens When You Shift Without Using Your Clutch?
Clutchless shifting is quite safe using the appropriate techniques, which means really just upshifting at the right RPM. But it’s risky in a downshift and generally can do damage to the transmission when mistimed.
What gear should I start a motorcycle in?
Best to start in neutral. When ready, pull in the clutch, shift to first gear while slowly releasing the clutch and applying throttle
